In recent years, the salvadoran economy has faced multiple challenges, but it has also shown positive signs that allow for an optimistic assessment of its evolution and prospects.
Alonso Zuniga / Photographer / Producer
Private Investment and Housing: A Key growing sector
One of the central themes is private investment, especially in the housing sector, which has shown considerable demand. The growth of the real estate market has boosted construction as an economic driver, although it faces a problem of insufficient supply that has caused a significant increase in housing prices. Larger-scale housing projects are being promoted, including towers of more than 35 floors, with the aim of expanding supply and stabilizing prices in the future.
Stable, albeit modest, economic growth
El Salvador maintains stable economic growth of around 2%, a figure that, while modest compared to other countries, is preferable to volatile or negative growth. Stable growth helps avoid sudden shocks to the economy and creates a solid foundation for sustained development.

International bonds and country risk perception
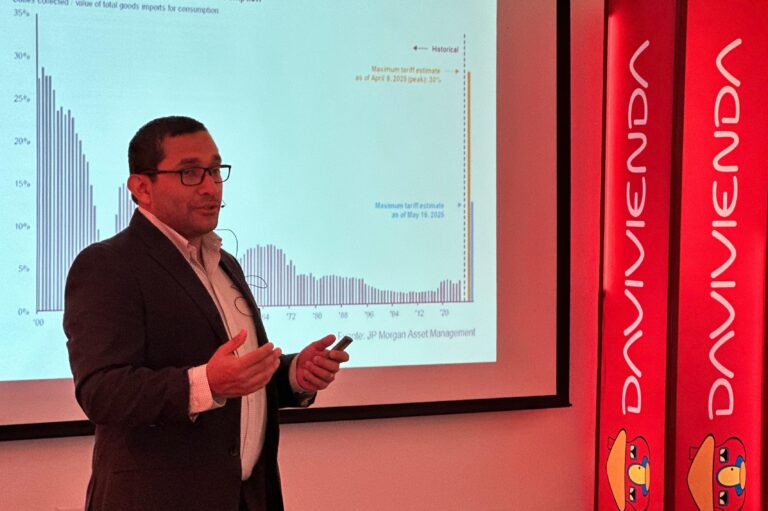
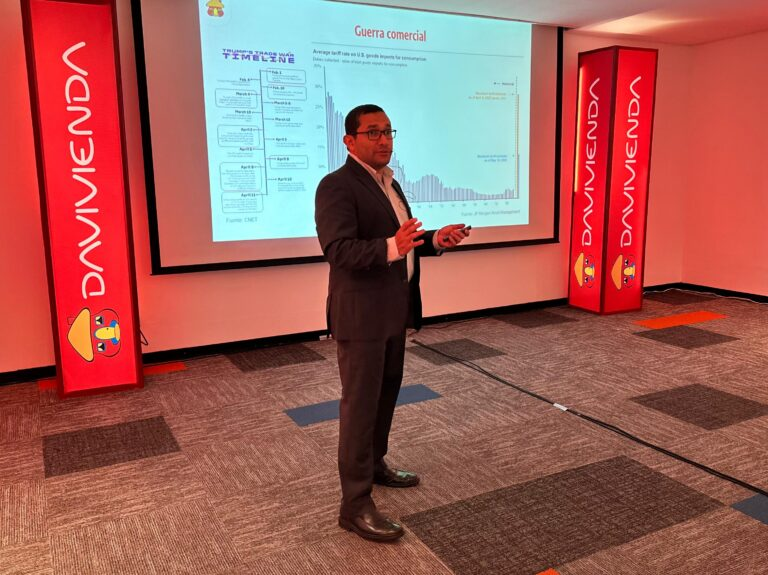
The performance of sovereign bonds is a key indicator of international confidence in the salvadoran economy. Since 2022, there has been a significant improvement in bond yields, which now stand in a more reasonable range between 7% and 9%, compared to much higher rates previously observed. Although volatility persists due to local and international factors, this positive trend indicates greater stability and the country’s ability to access international financing at reasonable costs.

Financial System: Growth and liquidity challenges
The salvadoran financial system is primarily composed of commercial banks, which represent 90% of the sector’s assets, along with cooperative banks and savings and loan associations. In 2024, the system showed solid growth in assets (7%), deposits (7-9%), and loans (3-8%). The average interest rate on loans remains around 10.6%, with variations depending on the type of financial institution.

However, cooperative banks face difficulties due to their higher cost of deposits and the need to raise interest rates to maintain their operations, which has affected their competitiveness. Savings and loan associations, meanwhile, operate with even higher interest rates due to their focus on specific markets.
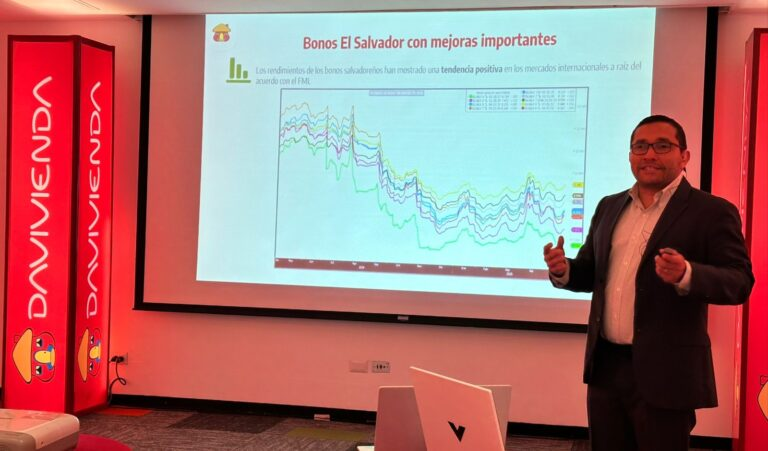
Commitments to the International Monetary Fund
The agreement with the IMF, signed in 2024 after years of delay, establishes key commitments to improve the country’s macroeconomic stability:
Fiscal consolidation: Control of public spending to achieve a budget surplus.
Strengthening bank reserves: Gradual increase in liquidity in the financial system for greater resilience.

Promoting sustainable investment: Encouraging projects that consider environmental and social aspects.
Transparency and fighting corruption: Improving accountability and strengthening institutions.
Efficient use of resources: Optimizing public spending to ensure positive results. These commitments seek to balance economic growth with the country’s fiscal and financial sustainability.







