The salvadoran financial system has shown significant strength in its liquidity levels, according to figures published as of july 2025.
The data shows that various institutions have strengthened their buffers to address potential shocks and build confidence in the sector, in line with the commitments made to the International Monetary Fund (IMF).

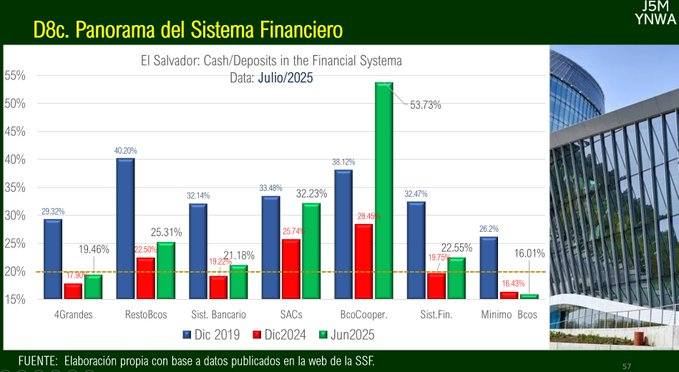
The four largest banks maintain a liquidity level close to 20% of total deposits, improving 1.56 percentage points in just seven months, reflecting prudent cash management.
Medium-sized banks (the remaining banks) have liquidity levels above 25%, strengthening their capacity to address unforeseen events.
SAC: Robust liquidity
Sociedades de Ahorro y Crédito (SACs) exceed 30% in liquidity, positioning themselves as solid players within the sector.
The performance of cooperative banks is noteworthy, with more than 50% in cash-to-deposits ratios, even reaching 53.73% according to the recent chart, marking the highest indicator and demonstrating “super liquidity”.
The bank with the lowest liquidity level stands at 16.01%, a value that, although low in comparison, remains within control margins and does not represent an immediate threat to stability.

Context and relevance for financial stability
These liquidity gains are the result of regulatory and supervisory measures aligned with the commitments made to the IMF to strengthen national macroeconomic and financial soundness.
In particular, the Central Bank raised reserve and liquid asset requirements, helping the entire system strengthen its positions against the risks of massive deposit withdrawals and external shocks.
The observed strengthening provides confidence to depositors and investors and represents a real capacity to respond to potential liquidity stresses, consolidating the goal of resilience of the salvadoran financial system.
advantages.

Advantages
- Increased bank liquidity in El Salvador has positive implications for the stability and soundness of the financial system, strengthening resilience to external shocks and improving depositor confidence.
- It enables banks to respond more effectively to potential massive deposit withdrawals, avoiding crises of confidence and potential bank runs.
- It reduces the risk of insolvency, ensuring that banking institutions can meet their immediate obligations, even in adverse scenarios.
- Access to Better Financing and Risk Reduction
- It helps improve the credit rating of the country and the banking sector, facilitating access to international financing on better terms for both the government and private banks.
- Greater liquidity signals robustness for investors and multilateral organizations, which can translate into lower funding costs and greater investment opportunities.







